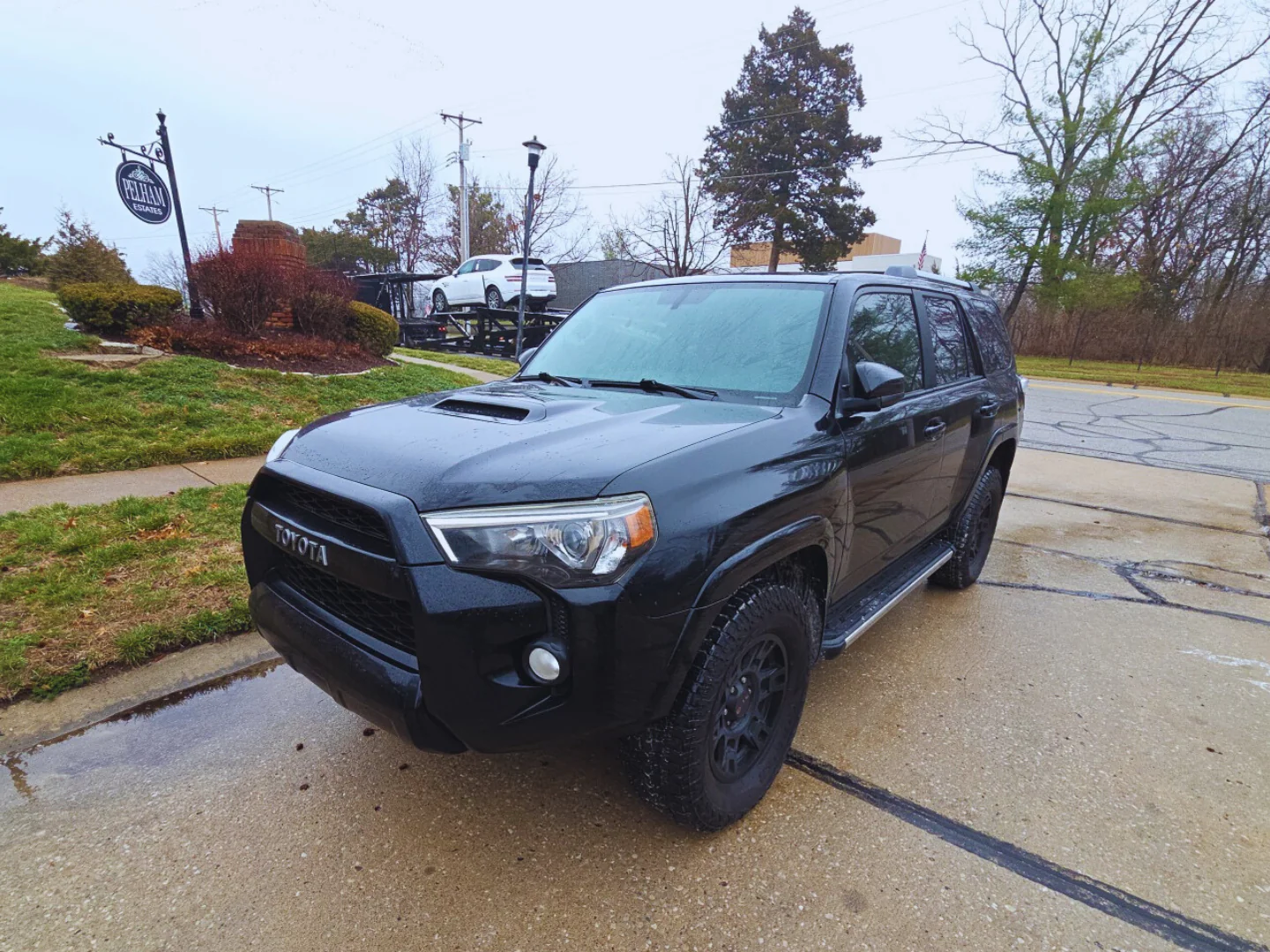
A Brand-New Toyota Sienna Delivered From Muscatine, IA to Minneapolis, MN
A customer from Minneapolis recently bought a brand-new Toyota Sienna from a dealership in Muscatine, Iowa. He didn’t want to drive 340 miles to pick it up himself so he called us to handle it. The final price was $600 for open auto transport and the van was picked up within 48 hours of booking.

That kind of turnaround doesn’t always happen on short-haul Midwest routes. Here’s a breakdown of what went into this shipment and what you should know before shipping a passenger van of your own.
What It Actually Costs to Ship a Passenger Van — and When $600 Is a Fair Price
The math on this shipment comes out to be $1.76 per mile. This is on the high end for an open transport shipment for a short-haul run under 500 miles. Typical sedans on this type of run tend to be more in the $0.90-$1.20 per mile range.
“Why does the price of the Sienna come in at this price point, at $1.76 per mile?”
Passenger vans are a larger product than the majority of the products carried on the deck of the transport vehicle. They take up more real estate on the deck. This impacts the number of cars the driver can carry in a single run. They factor this in when they are giving the price quote. If the price quote comes in at the price I quoted the customer today—$600—it’s because the vehicle is a full-size van and the run is from a small Midwest market.
When $600 is fair—and when it’s a red flag
A price quote of $600 for a 340-mile open transport run for a full-size van from a small Midwest market isn’t overkill. It’s the price the run and the vehicle size justify.
A red flag would be a price quote in the $300-$350 range for the same run. That’s the bait price they throw out there on the dispatch boards. No carrier would take this price and run the run. The shipment sits there and the days go by. The customer starts calling the brokers and saying, ‘Hey, I need this price raised up so I can get this shipment moving.’ But by then, you’re already committed.
Passenger Van vs. Sedan: Why Vans Cost More to Ship
The size difference between a Toyota Sienna and a standard sedan is the core reason vans cost more to ship. It’s not arbitrary — it’s math.
A typical 9-car open hauler loads vehicles based on available deck space and combined weight. A Sienna runs around 4,400 pounds and sits significantly longer and taller than a midsize sedan. Depending on configuration, it may load into a spot that would otherwise hold two smaller vehicles on certain trailers.

Why Shipping a Car From Muscatine, Iowa Is Harder Than You’d Expect
Muscatine is a small town in eastern Iowa near the Mississippi River. It is not a small town, and it is not near a carrier hub. This is more important than you might realize.
A carrier travels a certain route for a reason: it is a profitable route for the company. An individual driver will typically drive a certain route, like from Chicago to Denver, and will not take a 60-mile detour to pick up a vehicle in Muscatine, regardless of how many vehicles they are transporting, unless it is worth their time and money. And since most carriers drive routes near interstates like I-80 and I-90, a pick up in a secondary market like Muscatine means there are fewer drivers on the route for a given time period.
Fewer drivers on a route means there is less competition for the vehicle, and therefore the price is not going to come down as low as it might for a vehicle picked up in Des Moines or Chicago. This is one of the biggest things affecting auto transport prices, and it is one of the biggest things that catches customers off guard.
In this case, we were able to find a carrier within 48 hours because the Minneapolis route is a popular one with a lot of traffic. However, in a less populated time of year or in the middle of winter, it could take longer to move vehicles on this same route from Muscatine.

The bottom line for this shipment is as follows: the customer paid $600 for an open auto transport of his brand-new Toyota Sienna from a dealer in Muscatine, Iowa, to his home in Minneapolis, Minnesota. The vehicle was picked up within 48 hours and delivered safely. For this route, vehicle type, and market, the price is what it is – what it really costs to move the vehicle, without markup or without discount.
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Muscatine, IA to Minneapolis, MN
Muscatine, IA → U.S. Route 61 North → Interstate 80 West → Interstate 380 North →Interstate 35 North → Minneapolis, MN - Vehicle: 2026 Toyota Sienna
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Modification: No
- Service: Open Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: Passenger Van
- Shipping price: $600 ($1.75 per mile)
Shipping a Toyota 4Runner TRD From Jacksonville, FL to St. Louis, MO: What $500 Actually Covers
The 2015 Toyota 4Runner TRD is not your average mid-size SUV. It comes with serious ground clearance, a boxy build, and a TRD-tuned suspension that adds real weight to the equation. When this particular 4Runner needed to ship 900 miles, the final bill came to $500 and the pickup-to-delivery window was two days. That works out to $0.55 per mile which sits below what most people expect to pay for a vehicle this size.
Breaking Down the $0.55 Per Mile Rate: What’s Actually Included in Car Delivery Pricing
A lot of customers see a price of $0.55 per mile on a quote and think, “What’s the catch?” On this shipment, this price included the fuel costs of the carrier as well as the broker coordination fee.
Longer routes, of course, mean a lower price per mile as the carrier can create efficient routes over the major corridors of the country. A 900-mile route provides a good density of freight per vehicle, which the driver benefits from at the end of the route.
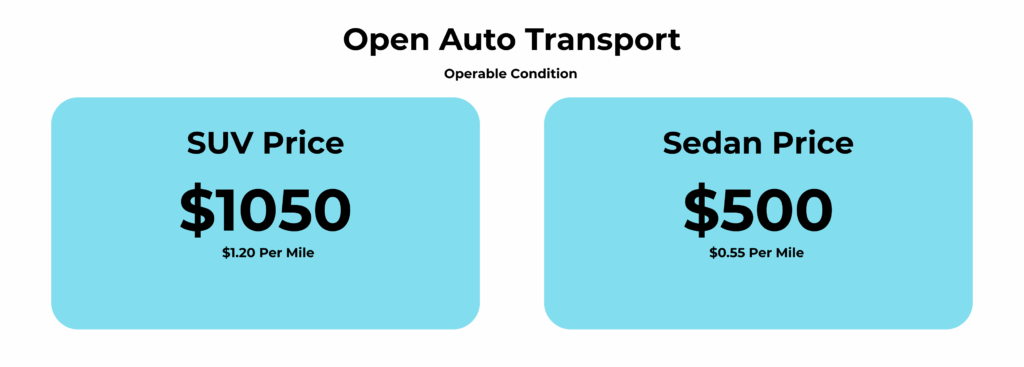
Most comparable open transport routes are going to be in the range of $0.75 to $1.20 per mile, but this 4Runner was well outside of this price range, which made it a great deal.
Estimated Price for Shipping a Vehicle from Florida to Missouri
How Open Trailer Auto Shipping Works for Rugged Mid-Size SUVs
Open transport is the standard choice for rugged mid-size SUVs because it is the most accessible and cost-effective method currently offered. An open hauler can carry anywhere from 7 to 10 vehicles at a time on a multi-level deck and makes use of fixed fold-up ramps to load the vehicles. The 4Runner drives up the ramps on its own power and is then strapped down at the four corners using axle straps.
The ground clearance of the TRD trim is far above 9 inches, so there is nothing to worry about in terms of scraping the ramps or the need for race ramps and tilt beds. This makes the loading process quick and efficient since the vehicle is a runner and has that kind of clearance to work with.
The TRD trim is heavier compared to the normal 4Runners, so the carriers will be placing it on the lower deck to maintain a balanced weight distribution for the full load.
Modified vs. Stock 4Runner Shipping: Surcharges, Restrictions, and Carrier Decisions

Carriers tend to make a clear distinction between a modified 4Runner and a standard 4Runner based on height and gross weight. A standard 4Runner typically has a height of 72 inches. A 2-inch lift puts this at a height of 74 inches.
Most open haulers place a soft ceiling at 78 to 80 inches in total height for upper deck placement, but this 4Runner was clearly above this standard with plenty of clearance to spare. Where a modified 4Runner begins to incur additional costs in money is when heavy aftermarket parts are added.
Steel bumpers, skid plates, and a fully loaded roof rack begin to increase the gross weight of a 4Runner, and a surcharge may be added to the bill if this increases the weight beyond standard limits for a specific deck placement.
How a 2-Inch Lift Affects Your 4Runner’s Open Transport Eligibility and Pricing
A 2-inch lift on a 4Runner poses no real complications in open transport. The standard clearance on this model of 4Runner is already close to 9 inches, so a 2-inch lift only puts the vehicle within a normal range of loading capacity. Carrier companies rarely complain about a mild lift kit on a vehicle already so tall.

A problem with height does occur, though, if a lift kit increases the height of a 4Runner beyond 4 inches, even on a tall platform like this model of 4Runner. At this point, the carrier begins checking the total height of the deck because of overpass clearance restrictions on some routes. A 2-inch lift on this model of 4Runner remains safely within the limits of an open hauler.
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Jacksonville, FL to St. Louis, MO
Jacksonville, FL → Interstate 10 West → Interstate 75 North → Interstate 24 West → Interstate 57 North → Interstate 64 West → St. Louis, MO - Vehicle: 2015 Toyota 4Runner
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Modification: 2 Inch Lifted
- Service: Open Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: Rugged Mid-Size SUV
- Shipping price: $500 ($0.55 per mile)
Luxury SUV from Rollinsford, NH to Indian Rocks Beach, FL: Route, Cost, and What Actually Affects the Price
A returning customer called our team again to get a quote for his 2020 BMW X7. The pickup was at a dealership in Rollinsford, New Hampshire. The destination was a residential address in Indian Rocks Beach, Florida. Total distance came out to 1,430 miles and the shipment was booked at $1,600.
This kind of route is one we handle regularly. It also brings up questions that come up often so understanding what goes into pricing on this corridor is worth walking through in detail.
What Information You Need Before Requesting an Enclosed Carrier Quote
Most customers lead with “how much will it cost?” That’s fair but the answer depends on specific details before any number is accurate.
For the BMW X7, the customer had the year, make, and model ready. That helped since the X7 is a full-size luxury SUV with weight and dimensions that affect how it fits on a trailer. The 2020 X7 weighs around 5,174 lbs and stretches over 203 inches in length. Not every enclosed hauler can fit a vehicle that size without careful planning around the other units loaded.
Beyond vehicle specs, carriers need to know the pickup and delivery addresses. They also need to know whether the car runs under its own power and whether any modifications affect the ground clearance. For enclosed quotes specifically, vehicle dimensions matter more than with open transport. Enclosed trailers carry fewer vehicles so every inch on the deck counts.
Timing also affects the quote. A pickup window of 3 to 5 days gives carriers more flexibility to plan. Tighter windows can push the price up depending on how much capacity is available on the route.
Why Dealer Transport Is Priced Differently
There is a difference between picking up at a dealership versus picking up at a residential driveway. With a dealership, there is less space to stage. There is also a release process that has to take place. The vehicle has to be cleared by a point of contact before it is picked up by the driver. Both the broker and the carrier have to document the status of the vehicle at the time of pickup.
In this particular load, the pickup at the dealership in Rollinsford was coordinated. The driver performed a standard inspection on the Bill of Lading before the X7 was picked up. This is to protect both the carrier and the customer in case of damage claims at a later time.
There is an additional consideration that has to take place with residential deliveries. Indian Rocks Beach is a Gulf Coast community. It is a barrier island, and there are narrow roads in that area. Narrow roads mean that a full-size carrier truck is not able to pull up to the residence. In that case, the driver would arrange to meet at a convenient spot to allow the customer to safely disembark from the truck. This is common in coastal communities.
See a Real Dealer Shipping Example
- Ferrari F12 Cross Country Shipping: Riviera Beach, FL to Fontana, CA
- Shipping an EV from a Dealer in Aurora, IL to a Private Buyer in Tallahassee, FL
Shipping a Car from New Hampshire to Florida: Route Overview
The distance between Rollinsford, New Hampshire, and Indian Rocks Beach, Florida, is approximately 1,430 miles. Most carriers will take I-95 South as the main route because it connects the Northeast region directly with the Central region of Florida, with the route diverging further south to the Gulf region.
New Hampshire is at the northern end of an important southbound shipping route, and Florida is an important destination for auto shipping services throughout the year. This makes it easy to find a southbound carrier to transport your vehicle. This is because there is constant activity in the region, especially during the winter season.

The estimated time to transport your vehicle along this route is between 3 to 6 days. However, the weather is the only factor that can affect the time it takes to transport your vehicle. Indian Rocks Beach is in Pinellas County, but the pickup is usually from the Tampa or Clearwater region.
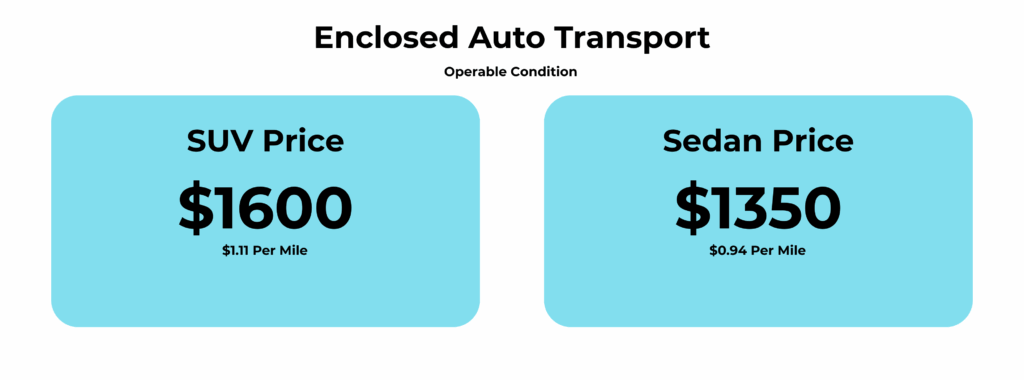
At an estimated cost of $1,600 for 1,430 miles, that comes out to an estimated cost of $1.12 per mile. This is within the standard range to transport your SUV either in an enclosed or open carrier from the Northeast region to Florida.
SUV vs Sedan Price Difference on this route
The X7 requires more deck space than a regular mid-size sedan, and this is the reason why SUVs are more expensive to transport. When the carrier is hauling 8 or 9 vehicles on an open trailer, the size and height of the vehicle are factors in the overall weight of the vehicle and the overall height of the loaded vehicle, which must not exceed the legal limit.
For a trip of approximately 1,400 miles, the cost of hauling a compact sedan will be between $1,000 and $1,400. A full-size SUV like the X7 will add another $200 to $400 due to the additional deck space required for the vehicle. Fuel consumption is another factor in the overall cost of hauling the vehicle, and this is factored in as well.
When hauling from New Hampshire to Florida, the type of vehicle is one of the major factors in the overall cost of the trip, after the distance. A full-size SUV will realistically be in the $1,400 to $1,700 range for the trip, depending on the time of year and the available carrier capacity at the time of booking.
Price Estimate for Shipping a Luxury SUV from New Hampshire to Florida
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Rollinsford, NH to Indian Rocks Beach, FL
Rollinsford, NH → 95 South through MA, CT, NY, NJ, DE, MD, VA, NC, SC, and GA → merge onto Interstate 4 West → connect to Florida State Road 688 West → Indian Rocks Beach, FL - Vehicle: 2020 BMW X7
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Enclosed Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: Full-Size Luxury SUV
- Shipping price: $1,600 ($1,11 per mile)
Range Rover Sport Shipping Cost: Frisco TX to Malibu CA for $550 (1,500 Miles)
We picked up a 2019 Land Rover Range Rover Sport in Frisco, Texas. It went to Malibu, California for $550 on open transport covering around 1,500 miles. This is one of the busiest westbound corridors in the country. Because this lane sees steady traffic, carriers were easy to find and the price stayed competitive.
Most people look at $550 and just see the cost. What they don’t see is everything that had to line up to make that number work.
Why Shipping a Full-Size Luxury SUV 1,500 Miles Takes More Than a Basic Order
The Range Rover Sport isn’t a compact car. At roughly 5,000 pounds, it takes up more room on a hauler than a standard sedan. Most open carriers hold up to nine vehicles. The way each one is loaded affects the whole trailer’s balance. A full-size SUV changes how the driver has to arrange that load from the start.
The route follows I-20 out of Frisco and connects to I-10 heading west. Those highways carry strong outbound freight from the Dallas-Fort Worth area. So finding a carrier on this lane is pretty reliable. DFW generates enough volume that dispatchers can match orders without much of a wait.
The $550 rate makes sense when you look at how this lane performs. Longer hauls don’t always cost more per mile because carriers want to fill trailers on busy corridors. For a 1,500-mile run from Texas to Southern California, $550 is a solid rate for open transport.
Open transport was the right call here. The Range Rover Sport didn’t need special protection since the route conditions were good. The vehicle was in solid shape and enclosed transport would’ve cost more without actually helping.
Full-Size SUV Price Estimate from Texas to California
| Transport Type | Vehicle Condition | Total Price | Price Per Mile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Auto Transport | Operable | $550 | $0.36 |
What Is a Bill of Lading and Why Is It Your Only Legal Protection During Auto Transport?
Before the Range Rover even rolled onto the carrier in Frisco, the driver performed a pre-load inspection. The Bill of Lading was completed and executed in accordance with the terms and conditions of Tempus Logix. This is not just a formality. This is the official record of your vehicle’s status at the time of change in ownership.
The BOL lists the make, model, VIN, and mileage. It lists each scratch, dent, or paint chip that was present before the vehicle ever hit the carrier. Both the driver and customer sign off before the vehicle is ever transported. This document is what supports or denies any damage claims at the time of delivery.
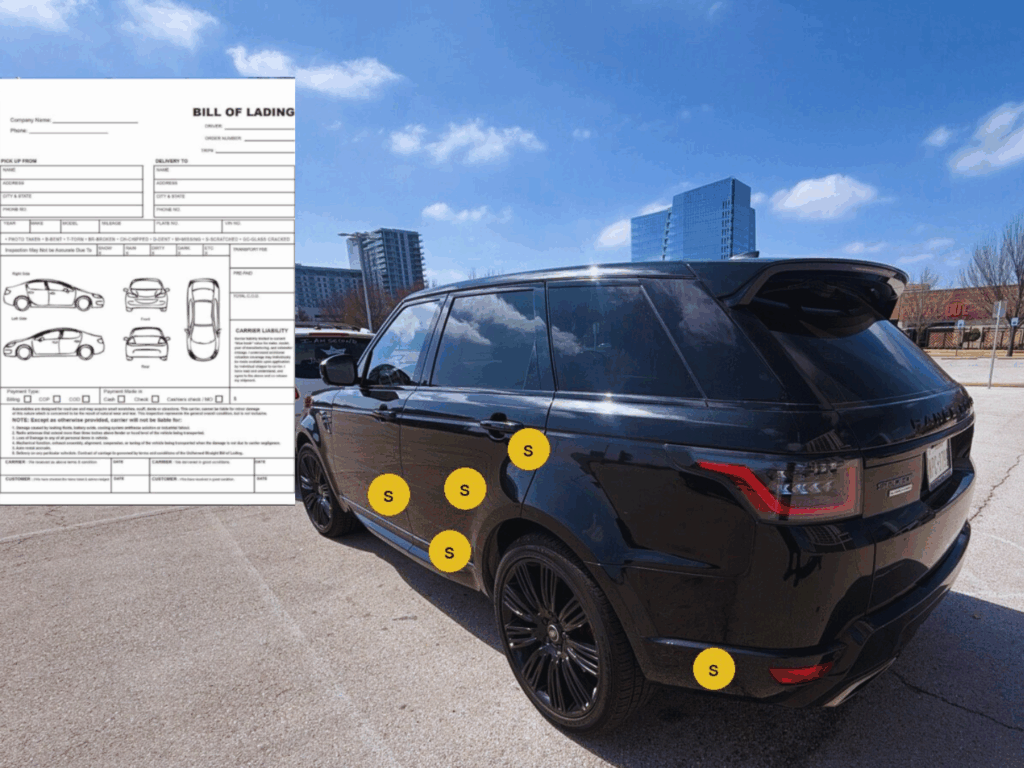
But what many people do not know is that the customer is supposed to sign the BOL without ever walking the vehicle. This is where the problems begin. If the driver marks an existing damage on the BOL and you did not review it at pickup time, you will find yourself in a world of trouble. This pre-existing damage is almost impossible to deny at the time of delivery.
Not walking the vehicle is probably the most common mistake in auto transport. It is just a few minutes at pickup time that will save you a world of trouble at the time of delivery.
The pickup inspection is the standard by which the delivery inspection is performed. What is documented on the BOL is exactly what is checked against at the time of the final walkthrough. Getting it right at the beginning is just as important as getting it right at the end.
See Also: Understanding About Auto Transport Bill of Lading
Understanding BOL Damage Codes

Delivering to Malibu: Coastal Access, Tight Streets, and the Last Mile
Malibu is not an easy delivery location. The Pacific Coast Highway runs through the city, and there are many residential streets that are off the PCH. These are not made for large, long trucks like the standard 9-car carrier. The sharp turns and the low clearance off the bluffs are not conducive for such large equipment.
Most neighborhoods in Malibu are located at the end of access roads that are off the canyon. These are not made for large equipment, so full-size carriers cannot get to the exact delivery location. The carrier and the customer agree on a meeting point, and the customer picks up the shipment from there. This is the standard practice for the area, and most customers in Malibu are aware of the practice. The driver calls ahead to confirm that access is allowed.
For the shipment, the driver and the customer agreed on a pull-off near the PCH. The Range Rover was picked up without any issues. The final BOL was done, and the driver and the customer confirmed that everything was in order.
The rate of $550 for the shipment of 1,500 miles from Texas to the West Coast of California is good. The key is that the BOL is kept accurate at both ends of the shipment. Otherwise, the rate could go through the roof.
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Frisco TX to Malibu CA (1500 miles)
Frisco, TX → Dallas, TX → I-20 W → I-10 W → Los Angeles, CA → Malibu, CA - Vehicle: 2019 Land Rover Range Rover Sport
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Open Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: Full-Size SUV
- Shipping price: $550 ($0.36per mile)
Shipping Guides of Our Company:
Delivery of a Super Car Corvette from Sherman Oaks, CA to Berkeley, MO
A customer from Sherman Oaks called us about his 2022 Chevrolet Corvette. He needed it shipped to Berkeley, MO. That’s 1,850 miles. And it was clear from the start this car couldn’t go on just any trailer.
The Corvette made it to Berkeley in three days. The total cost was $1,700, which comes out to $0.91 per mile. Here’s how the whole thing went.
Price Estimate For Enclosed Sport Car From California to Missouri
| Transport Type | Vehicle Condition | Total Price | Price Per Mile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosed Auto Transport | Operable | $1700 | $0.91 |
Why Enclosed Transport Was the Only Option for This Corvette
The 2022 Corvette sits at about 4.3 inches of ground clearance. The front splitter sits even lower. Standard open trailers use steep ramps to load vehicles. That angle alone is enough to scrape the splitter before the car even reaches the deck.
We matched this shipment with an enclosed multi-car trailer built for sports cars and low-clearance vehicles. It carries fewer cars than a standard nine-car open carrier so each vehicle gets more space on the deck.
The walls and roof protect the car from road debris and weather for the full 1,850 miles. That really matters on a cross-country run because February weather between California and Missouri is anything but predictable.
See Also: V8 Sport Car Enclosed Shipping։ Riverside CA to Suffolk VA
What sets this trailer apart is the hydraulic liftgate. No ramps. The platform drops all the way to the ground so the Corvette drives onto a flat surface. The liftgate then lifts the car up to the deck slowly and under full control. There’s no steep angle and no risk of scraping the undercarriage or front splitter. For a car like this, it’s the only way to load it. That $1,700 covers the enclosed trailer and liftgate loading as well as door-to-door handling between two private residential addresses.
The Inspection at Pickup and How the BOL Works
The driver showed up at a residential street in Sherman Oaks. Before anything got loaded, he did a full walkaround inspection right there on the spot.
He recorded a video while walking around the car. He checked both bumpers and paid close attention to the front splitter. He also confirmed the condition underneath the car. Any existing marks went into the Bill of Lading before loading began. The BOL is the official condition record for the shipment. It documents the car’s state at pickup and again at delivery. Both sides have a clear reference if anything comes up later.
Once the BOL was signed, we loaded the Corvette using the hydraulic liftgate. Soft tie-downs secured the car on the deck since they protect the finish and won’t damage the lower panels. The trailer pulled out of the neighborhood without any issues.
Guide to BOL: Understanding About Auto Transport Bill of Lading
The Drive from Sherman Oaks to Berkeley and How Long It Took
The route runs through the Southwest and up into the Midwest. February in that stretch can bring ice through parts of Texas and Oklahoma. Missouri can get hit too depending on the week.
We gave the customer an estimated delivery date of February 27th. The Corvette arrived on February 26th, one day early. The driver covered 1,850 miles in three days.
That kind of timing is realistic on this corridor because it connects two busy regions. Carriers on this route have solid coverage so dispatch tends to be quicker than on more rural runs. Winter weather added some uncertainty but conditions held up and the driver kept moving.
At delivery, the owner did a final walkaround and compared everything against the pickup BOL. Everything matched. He signed off and the Corvette was back in his hands at his address in Berkeley, MO.

Shipping Summary
- Direction: Sherman Oaks, CA to Berkeley, MO
Sherman Oaks, CA→ I-405 N → I-5 N → I-15 N → I-70 E to Berkeley, MO. - Vehicles: 2022 Chevrolet Corvette
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Enclosed Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: Sport Car
- Shipping price: $1700 ($0.91 per mile)
Shipping Guides of Our Company:
Shipping a 1,000-HP Muscle Car and a Grand Cherokee SRT from Tampa to Waxahachie
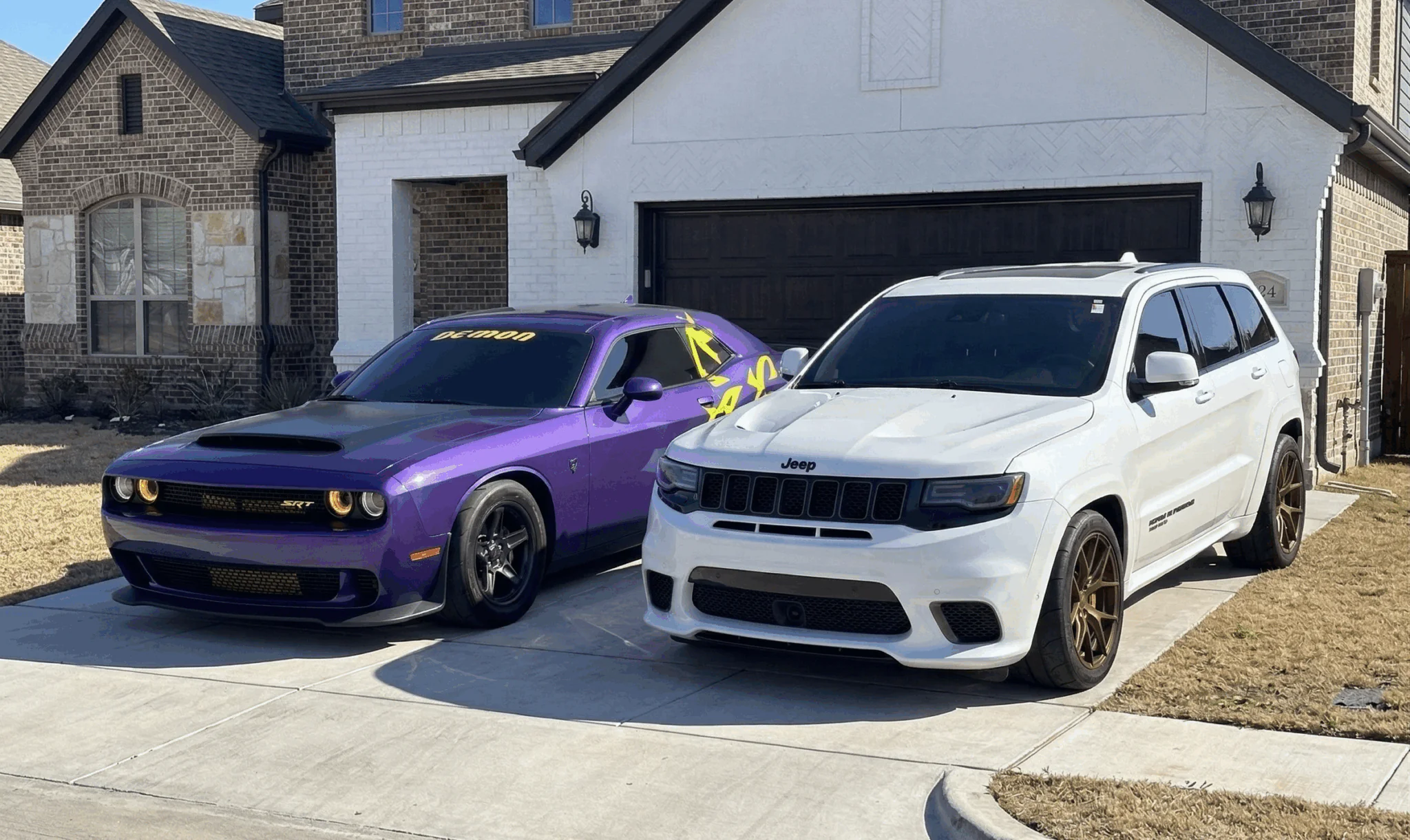
Not every load is a standard sedan going from point A to point B. This load was different. A customer out of Tampa, Florida, needed a 2022 Jeep Grand Cherokee SRT and a 2023 Dodge Challenger SRT Demon 170 transported to Waxahachie, Texas. This load’s planning began before a truck ever hauled it.
These aren’t cars you load and forget about.
Open VS Enclosed Trailer for 1,000-Horsepower Muscle Car
The 2023 Dodge Challenger SRT Demon 170 is a limited-production vehicle. This car was made by Dodge as a farewell to their Challenger model. With a limited production run, this car is already out of the value range of 99% of car owners. Then there’s the fact that it has 1,025 horsepower. This car is a collector’s item, and collectors want it protected. Open transport has never been an option for this vehicle.
Both vehicles are also equipped with performance tires. Performance tires are meant for racing and are meant to be on a track, not on a public road. Performance tires have a smaller profile and sit very close to the road. This means they pick up road debris before they even come into contact with it. On an open trailer traveling down a highway at 65 mph through Louisiana, road debris is a big concern for a car’s paint and brakes.
Price estimates
Open transport
$1,800–$1,900
Average: $1,850
Enclosed transport
$2,600–$2,800
Average: $2,700
Estimates vary by vehicle, season, and exact pickup and delivery locations. All estimates shown are for a standard sedan.
An enclosed trailer provides a barrier between your vehicle and road debris. This is especially important for a limited-production vehicle, as a scratched door or a rock chip can greatly impact a vehicle’s value. Tempus Logix picked up both vehicles at a private residence in Tampa, Florida, and dropped off both vehicles at a private residence in Waxahachie, Texas. There were no terminals or strangers involved.
See Also:
- Atlanta to San Francisco Bay Area Car Transport of a Challenger SXT
- Enclosed Lamborghini Huracan EVO Transport from Encino CA to Bozeman MT
Is $2,600 Fair for Two Cars on an Enclosed Trailer?
The short answer is yes. Here’s how open and enclosed pricing compared for this specific shipment.
| Transport Type | Estimated Cost | Price Per Mile |
| Open Carrier (Multi Car Hauler) | $1,800 – $1,900 | $1.6-$1.7 |
| Enclosed Carrier (2 vehicles) | $2,600 | $2.32 |
| Price Difference | ~$700 – $800 | – |
Spending an extra $700 to $800 to protect a car with that kind of value makes sense. A single repaint on a car like the Demon 170 could easily run more than the price gap between open and enclosed shipping. For performance vehicles with low ground clearance and soft compound tires, enclosed isn’t a luxury. It’s the right call.
Tampa, FL to Waxahachie, TX: Understanding the I-10 Corridor
This is a well-trodden road for carriers that travel between Florida and Texas. The route goes west on I-10, passing through Pensacola and New Orleans, and then turns north, passing through Houston and into the Dallas metropolitan area. Waxahachie is just south of Dallas from there.
This is one of the most traveled corridors in the country, and the I-10 corridor is no exception. Enclosed carriers make regular trips on this corridor, especially for high-value shipments headed into Texas, so the scheduling is always well-managed.
Tempus Logix picked up both vehicles on the 19th and delivered them on the 21st of February. Two days for a 1,120-mile trip in an enclosed trailer is a great job by the carriers. The standard transit time for a trip like this is between three and five days, depending on the carriers that are available and how many stops are made along the way.
This route takes carriers down a well-trodden road the entire way, so there were no stops to weigh the vehicles or take a scenic route that added to the overall transit time.
Delivery Day in Waxahachie: Post-Transport Inspection and What to Do If Damage Occurs
When the carrier arrived at the private address in Waxahachie, the customer was there for the unload. That’s always the right move.
Both vehicles came down the ramp and got checked against the original Bill of Lading from pickup. The BOL records the car’s condition before it goes on the truck so any comparison at delivery is based on fact. Scratches, paint chips or any new marks show up clearly when you know what was there before.
If damage does show up during transport, the process isn’t complicated. Note it on the delivery BOL before signing. Signing an unmarked BOL and then trying to file a claim later just makes everything harder. Take photos right at delivery and contact your transport company the same day.
In this case both vehicles arrived in the same condition they left Tampa. The Demon 170 rolled off the ramp looking exactly like it should.
Useful to Read: Understanding About Auto Transport Bill of Lading

Shipping Summary
- Direction: Tampa, FL to Waxahachie, TX
Tampa, FL to I-75 N → I-10 W → I-49 N → I-20 W → US-287 N to Waxahachie, TX - Vehicles: 2023 Dodge Challenger SRT Demon 170 & Jeep Grand Cherokee SRT
- Modification: SRT and SRT Demon 170
- Conditions: Both Run and Drive
- Service: Enclosed Auto Transport
- Vehicle type: SUV and Muscle Car
- Shipping price: $2600 ($2.32 per mile)
Shipping Guides of Our Company:
Shipping an EV from a Dealer in Aurora, IL to a Private Buyer in Tallahassee, FL
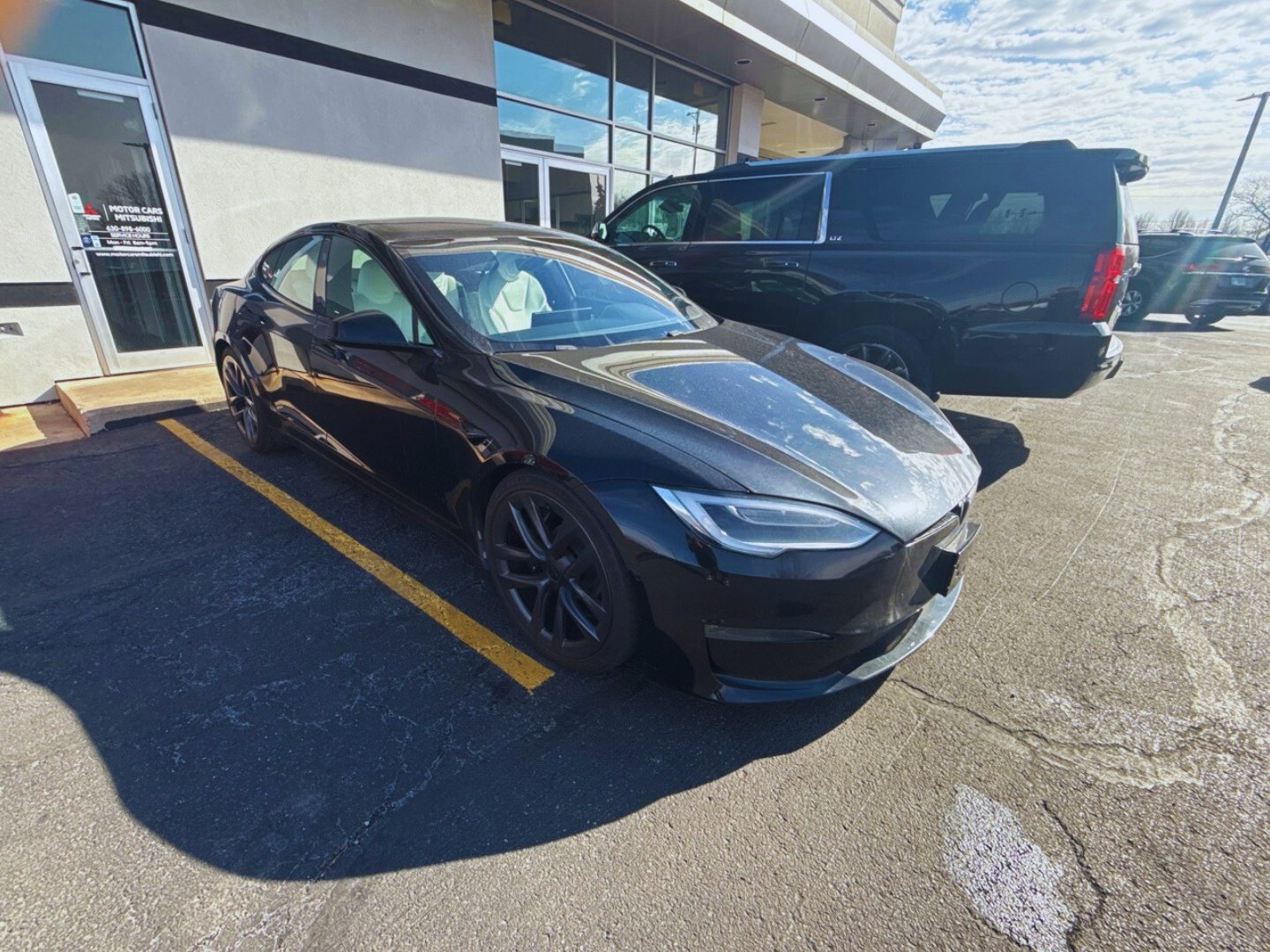
A dealer in Aurora had a 2022 Tesla Model S ready for a private buyer in Tallahassee. The buyer wasn’t local so Tempus Logix handled everything from carrier assignment to delivery sign-off. Here’s what that shipment actually looked like from start to finish.
Another Tesla Was Shipped By Our Company: 2024 Tesla Model Y Ships from Virginia to Mississippi
Why Shipping an Electric Vehicle Isn’t the Same as Shipping a Regular Car
A 2022 Tesla Model S weighs about 4,561 pounds. This is about 900 pounds more than a gas-powered sedan of similar size, owing to the battery pack on the floor of the car. This affects how the shipping company will be able to distribute the weight on the trailer.
Another difference is the ground clearance of the Tesla, which sits about 4.6 inches off the ground. This means that, unless the shipping company is familiar with shipping such vehicles, the front of the car will touch down on the ramp before the rest of the car is off the ground. This means that the approach angle of the ramp will not be a problem.
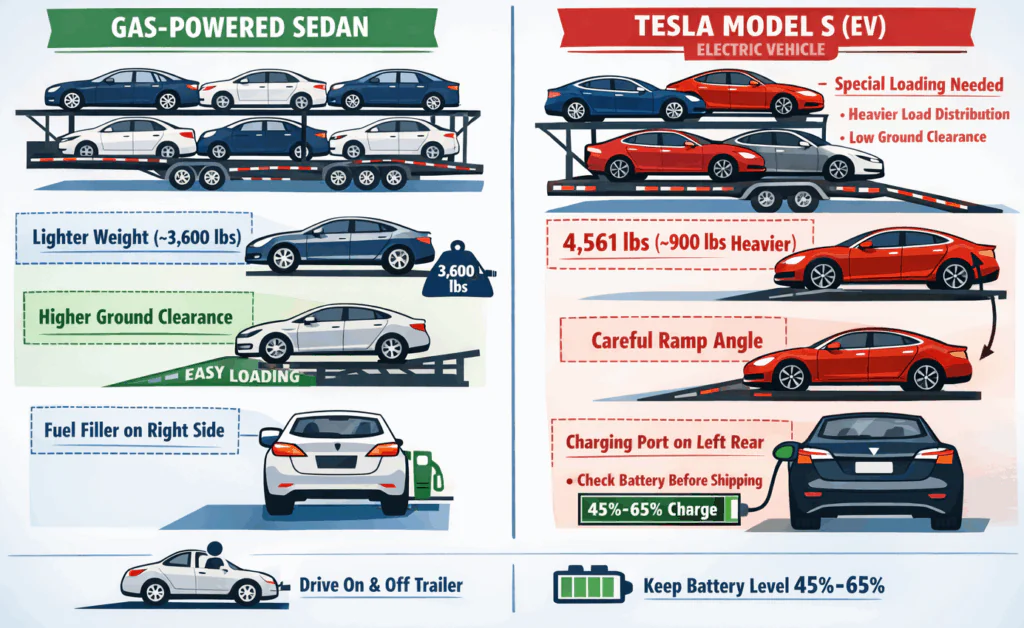
The charging port of the car is also located on the left rear quarter of the car, which means that, if the car is on the upper deck of an open trailer, it will be completely obstructed, so drivers will need to check the battery level before shipping the vehicle.
The car will also need to be driven on and off the trailer, so the customer should be told to keep the battery level between 45% and 65%. This gives enough power to move the car without risking heat buildup during shipping.
How Seasonal Demand, Fuel Costs, and the Aurora-to-Tallahassee Route Affect Your Final Price
The world of auto transport is a rapidly changing environment. Our transport agents have witnessed rates fluctuate within a single day based on the number of available transporters in a specific route. The transport was arranged in late spring when transport demand is high from the Midwest.
These aren’t surprises we want customers to run into without any heads-up. We do our best to hold the agreed price. But on longer hauls a small extra cost can occasionally show up and we’ll always flag it clearly before anything changes.
Open Auto Transport Price for EV from Illinois to Florida
Aurora, IL to Tallahassee, FL: Route, Transit Time, and Carrier Availability
To get to Tallahassee, the natural route south out of Aurora would take us down I-65, which passes through the Chicago suburbs. This is one of the most heavily used shipping routes in the country. It passes south of Indianapolis, Louisville, then on down into Birmingham, then southeast into northern Florida, ultimately terminating in Tallahassee. The carriers are readily available on this route since so much shipping occurs on it daily.
Under FMCSA regulations, a driver can only be on duty for 14 hours, of which only 11 can be spent behind the wheel. After 8 consecutive hours, the driver also has to take a 30-minute break. This translates into about 450 miles per day, which is the amount of ground we can cover on a daily basis. For 1,150 miles, we can expect 3-4 days for delivery, although weather can cause delays of one additional day, so we always quote a window of delivery.

How to Coordinate Carrier Pickup at a Dealership Without Being Present in Aurora
We weren’t able to be present in Aurora, so we worked with the dealership to arrange pickup. Before the driver arrived, we called the dealership to confirm their pickup window and who we should be working with. We also double-checked the VIN since they had multiple Model S’s on the lot. The last thing anyone wants is the wrong car being picked up.
Upon pickup, the driver took photos of the Tesla from multiple angles, then the dealer’s representative signed off on the Bill of Lading as the releasing party. We then forwarded a copy of the BOL to the buyer so he could review it prior to delivery. He did his due diligence, taking photos of the Tesla against the original photos taken during pickup, then signing off on the BOL once he had inspected the vehicle.
See Also: Understanding About Auto Transport Bill of Lading
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Aurora, IL to Tallahassee, FL
Aurora, IL → I-88 E → I-294 S → I-80 E → I-65 S → I-24 E → I-75 S → I-10 E → Tallahassee, FL - Vehicle: 2022 Tesla Model S
- Modification: Factory
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Open Auto Transport
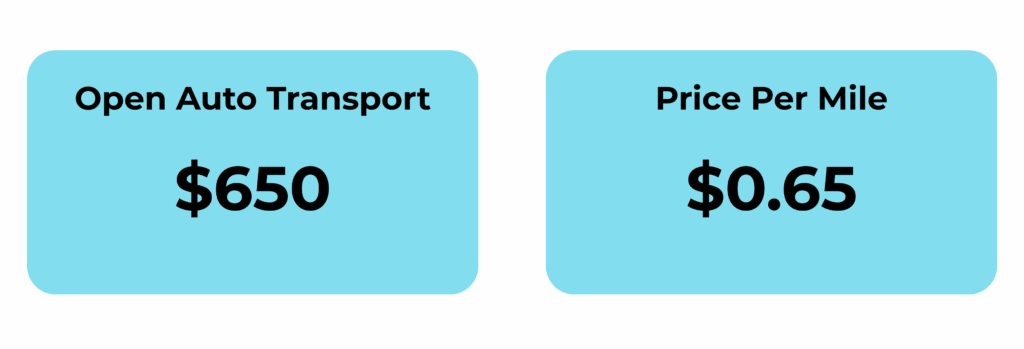
- Vehicle type: EV
- Shipping price: $650 ($0.65 per mile)
Shipping Guides of Our Company:
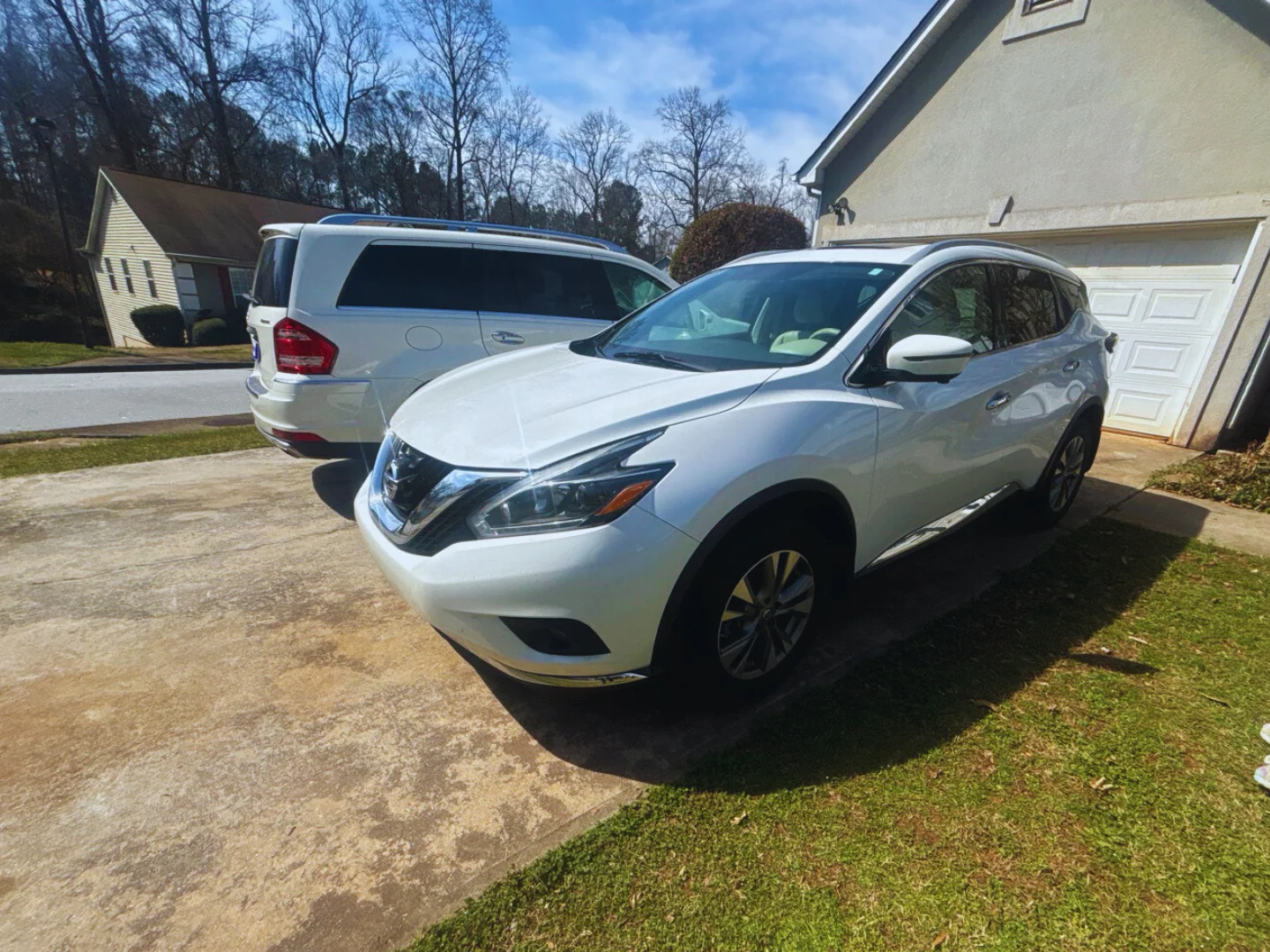
Mid-Size SUV from Decatur GA to Lexington KY in One Day
A 2018 Nissan Murano was picked up from a private address in Georgia on February 28. It was delivered to a private residence in Kentucky the very next day. The total came to $550 for 390 miles at $1.40 per mile. Here’s how that shipment came together.
How Residential Car Shipping Actually Works
Door-to-door shipping means the carrier comes directly to your pickup address. There’s no terminal drop-off and no driving to a hub across town. Tempus Logix handles all the coordination so the only thing you manage is being available at both ends.
Once you book with Tempus Logix, we assign a carrier and confirm both addresses. The driver arrives within the agreed pickup window and loads your car on-site. From there it ships directly to the destination without any extra steps on your end. You coordinate once and the rest is handled.
This works especially well for private customers because it cuts out the extra back-and-forth that terminal-to-terminal shipping involves.
See Also: Dealer Auto Transport Services
Is $550 a Fair Price to Ship a Mid-Size SUV from Georgia to Kentucky?
Short answer- Yes. At 390 miles and $1.40 per mile, the $550 total is a fair market rate for Georgia to Kentucky. Mid-size SUVs take up more deck space than a regular sedan so the per-mile rate reflects that. Open transport on a busy corridor like I-75 keeps the cost down without affecting service quality.
Rates shift based on the season and how many carriers are running the route. This one was booked in late February, which is typically a steady pricing period along Southeast routes.
Price Estimate For a Mid-Size SUV From Georgia to Kentucky

How a Mid-Size SUV Gets Loaded and Secured on an Open Carrier
Open carriers use a hydraulic two-deck system to load vehicles. The back half of the top deck lowers to form a ramp. Cars are driven up onto the metal treads and the deck raises back to its standard position. The lower deck works the same way.
For the Murano, the driver checked ground clearance before loading since standard ramp angles are fine for mid-size SUVs. Once on the carrier, tie-down straps were attached at four points on the vehicle. Those straps connect to the wheel wells and the matching chassis points. Tension gets adjusted until the car is fully locked in place.
That four-point setup holds throughout the entire route. A properly strapped mid-size SUV won’t shift on an open carrier no matter what road conditions it runs into.
The I-75 Corridor: Why This Route Is One of the Most Trafficked Auto Transport Lanes in the Southeast
I-75 connects Georgia and Kentucky through one of the busiest shipping lanes in the Southeast. Carriers run this corridor constantly because it links major cities like Atlanta and Louisville. That volume keeps prices reasonable and shortens wait times for customers going in either direction.
Truck traffic on I-75 stays consistent year-round so pickups along this lane happen faster than on quieter routes. That’s the main reason this Murano was picked up and delivered within 24 hours. On a less active route, two to three extra days could easily have been added to the timeline.
What to Do If You Find Damage After Open Transport Delivery
Start with a full inspection before signing the Bill of Lading. That document records the vehicle’s condition at both pickup and delivery. It’s the most important thing you have if any damage shows up after drop-off.
If you spot something new, note it on the document while the driver is still there. Don’t sign until it’s written down. Take photos right at the delivery site. Then contact the carrier to file a claim with their cargo insurance as soon as you can. Waiting a few days can make the whole thing harder so acting right away is the smarter move.
Hold onto all your pre-shipping photos from before pickup. Those images are your baseline and carry the most weight if the claim goes to review.
Useful Topics:
- What Happens If a Vehicle is Damaged During Transport
- Understanding About Auto Transport Bill of Lading
Transport Summary
- Direction: Decatur GA to Lexington KY
Decatur, GA take I-20 W to I-75 N, continue on I-75 N toward Kentucky, then take exit 113 to merge onto I-64 E toward Lexington, KY - Vehicle: 2018 Nissan Murano
- Modification: Factory
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Open Auto Transport
- Shipping price: $550 ($1,4 per mile)
Shipping a Full-Size SUV from Odessa, TX to Houston, TX
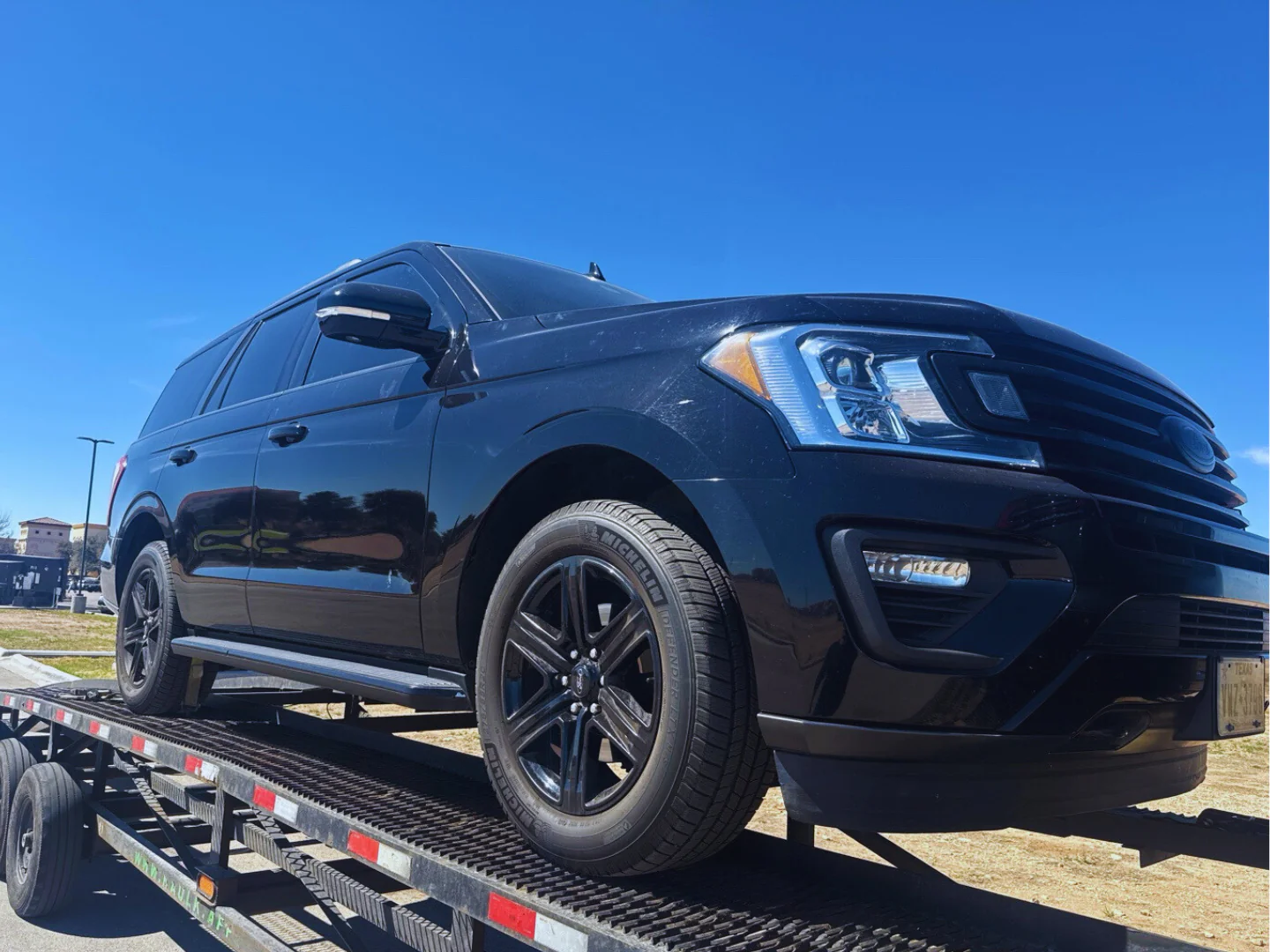
A 2020 Ford Expedition left a private driveway in Odessa on February 28 and arrived at a private residence in Houston the same evening. The shipment covered 540 miles at $0.65 per mile and came out to $350 total. For a full-size SUV moving across Texas, that’s a fair number. Here’s what actually went into making that happen.
What “Residential Area Pickup” Means for Auto Transport Carriers
Picking up from a private address sounds simple. In practice, it adds a few real complications that most people don’t think about until a driver is already on the way.
Full-size auto haulers are long. A standard nine-car carrier can stretch over 75 feet. Tight residential streets, low-hanging trees, and narrow driveways can make maneuvering difficult or even impossible. Drivers often need to stop at a nearby intersection and have the vehicle driven or pushed to meet them there.
With a 2020 Ford Expedition, the size of the vehicle itself adds another layer. It’s a large three-row SUV with a high roofline so its position on the carrier has to be planned carefully. Carriers avoid placing taller vehicles in spots where height clearance could be a problem during the haul.
That’s why the carrier assigned to this shipment did a quick route review before arriving. Confirming street access ahead of time avoids delays and keeps the pickup on schedule. Tempus Logix handles this coordination as part of the door-to-door service so the customer doesn’t have to figure it out independently.
See Also: Texas Car Shipping Services
Hotshot Hauling vs. Multi-Car Carrier: Which Is Better for Shipping a Large SUV?
For a 540-mile route like Odessa to Houston, the carrier type makes a real difference in timing and price.
A hotshot hauler is a single pickup truck pulling a smaller flatbed trailer. It typically carries one to three vehicles at a time. Because the load is lighter and the truck is more maneuverable, hotshot carriers can move fast on shorter routes. They’re also easier to route through residential streets since the truck and trailer combination is far more compact than a full nine-car hauler.
A multi-car carrier, by contrast, works best when the distance is longer and the route is a major corridor. Filling up nine or ten spots makes the haul financially worthwhile for the driver. On a shorter distance like 540 miles, a multi-car carrier may take longer to depart since the driver needs to fill remaining spots before rolling out.
For this particular shipment the carrier was selected based on route efficiency and same-day delivery requirements. The right fit at the right time made the difference.
How Much Does It Cost to Ship an SUV 500 Miles in Texas?
The Expedition shipment came in at $350 for 540 miles which works out to $0.65 per mile. That’s within the standard range for open transport on a Texas corridor route.
Pricing for SUV shipments depends on vehicle size, transport type, route demand, and timing. Getting an accurate number upfront matters because estimates that don’t account for vehicle dimensions or fuel costs tend to shift later.
Tempus Logix offers an AI-powered price calculator on its website that factors in pickup and delivery zip codes along with vehicle type to generate a real estimate. It’s worth running the numbers before making any decisions since pricing on popular Texas routes like this one can shift week to week based on carrier availability.
Price Estimate For a Full-Size SUV In Texas

How to Choose a Trustworthy SUV Shipping Company in Texas
Texas has a large auto transport market and not every company operating in it holds the proper credentials. Before booking with anyone, the first step is checking their FMCSA registration. Every legitimate carrier or broker operating in the US must be registered with the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration. You can verify a company’s MC number directly at safer.fmcsa.dot.gov.
Beyond the license check, customer feedback tells you what the paperwork doesn’t. Reading reviews on Google, Transport Reviews, and the Better Business Bureau gives a clearer picture of how a company actually handles pickups, delays, and communication.
For this Odessa to Houston shipment, the pickup happened on schedule and the Expedition arrived the same day in the same condition it left in. The Bill of Lading was completed at pickup and matched at delivery. That’s the standard to hold any carrier to.
Tempus Logix works with FMCSA-registered carriers and provides customers with carrier information before pickup day so there are no surprises.
See Also Our Car Shipping Guides:
- Houston to Dallas Car Shipping: Professional Relocation Guide
- Houston to Austin Car Shipping: The Complete Relocation Guide
- Houston to San Antonio Car Shipping | Relocation Guide
Shipping Summary
- Direction: Odessa, TX to Houston, TX
- Vehicle: 2020 Ford Exedition
- Modification: Factory
- Condition: Runs and Drives
- Service: Open Auto Transport
- Shipping price: $350 ($0.65 per mile)
B9.5 Generation Shipped from Bangor, ME to Dayton, OH
There are many variables to consider when shipping a sedan from northern Maine to Ohio during the month of February. The route takes you through some of the most weather-sensitive areas of the country during the middle of winter. When the customer came to Tempus Logix with the need to have their 2020 Audi A4 transported from Bangor, ME to Dayton, OH, the team got to work the same day the order was received.
This is a breakdown of how the shipment was handled, the decisions made, and the reason for the timeline of the shipment.
The Timeline
The order was booked on February 17, and the earliest available date was set for the same day. The carrier was assigned on February 20, three days after the booking. Pickup occurred on February 23, and delivery took place on February 24.
The total time elapsed from booking to delivery was seven days.
Three days between booking and assignment is quite normal, as dispatchers need time to assign each shipment to the appropriate carrier. Route type and time both play a role in this. Since this route passes through heavy freight routes, it didn’t take long to assign a carrier.
Between the assignment on the 20th and the pickup on the 23rd, the schedule was coordinated with the customer and other pickups along the route were accomplished. Open carriers typically load seven to nine cars on a single run, so the pickup order must be coordinated. The A4 was picked up in Bangor on the 23rd.
One day transit was required. The driver made the entire route from Bangor to Dayton and delivered the car on the 24th. The DOT limits daily driving to 11 hours, so a direct route such as this one need careful route planning to meet these requirements and arrive on schedule.
The Route: Bangor, ME to Dayton, OH
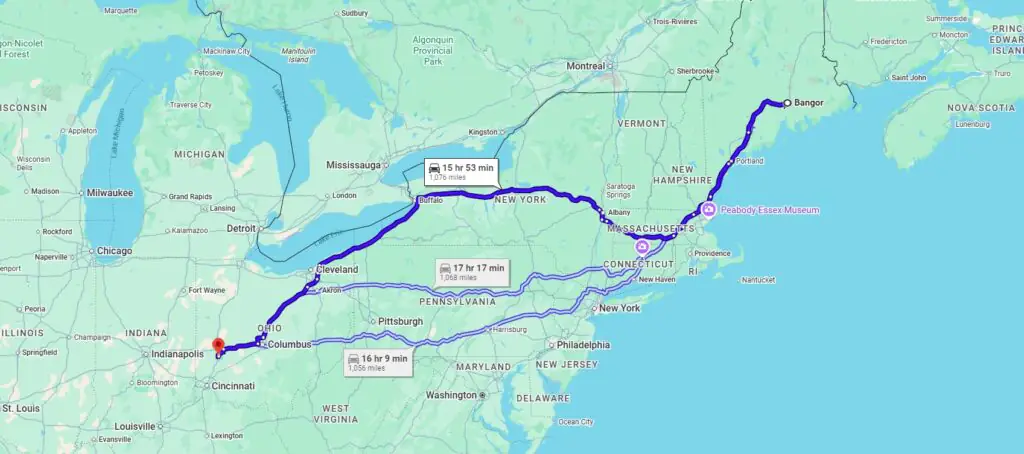
The distance between Bangor and Dayton spans approximately 1,100 miles. The route passes through the Northeast corridor and down through New York and Pennsylvania before finally arriving in Ohio. This is a freight route with regular carrier traffic, so it remains navigable even during the colder winter months.February is the peak month for winter in New England. For carriers out of Maine, the roads are icy, so the speed is slower. Choosing a carrier that is familiar with the Northeast is not simply a choice based on preference. It is one that impacts the way the entire process is handled.
Trailer Selection

Open transport was the correct decision for this transport. It is a good, solid sedan, not a classic or exotic vehicle that requires the added protection of an enclosed transport. It is also faster to schedule, as many more open transport vehicles are on the road. Additionally, the cost savings of open transport versus enclosed are significant.
The transport company used a standard multi-car transport vehicle. Cars are chained down using the axle straps and chains so that the vehicle does not move during transport. The A4 was chained down according to DOT regulations before leaving Bangor.
Some customers want to know about the exposure to the elements with the open transport in the winter. The way the vehicle is chained down ensures that it does not move regardless of road conditions. Some road salt or slush on the road is normal in February, but it washes off easily. There is no damage from the elements on a vehicle such as the A4.
Transport Summary
- Origin: Bangor, ME 04401
- Destination: Dayton, OH 45409
- Vehicle: 2020 Audi A4 (Operable)
- Distance: ~1,100 miles
- Primary routes: I-95 S → I-90 W → I-76 W → I-70 W
- Trailer type: Open trailer
- Season: Late February
- Price: $1,260 (~$1.15 per mile)